NEURO-DEGENERATIVE DISEASES
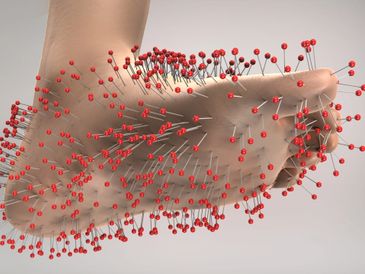
NEUROPATHY
Neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body. Damage to these nerves can result in various symptoms, including numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and pain, primarily affecting th
Neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body. Damage to these nerves can result in various symptoms, including numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and pain, primarily affecting the hands and feet.
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy:
While there are over 100 causes to neuropathy, it can be caused by a variety of factors including diabetes, which is one of the most common causes, leading to high blood sugar levels that damage nerves over time. Other causes include traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic problems, inherited causes, exposure to toxins, and many more.
Floods the tissues with photons, energizing the damaged cells and increasing blood circulation to painful areas, creating new blood vessels to reverse your condition.
By understanding how neuropathy affects balance, targeted therapies can be implemented to restore nerve health, strengthen muscles, and improve proprioception. Early intervention not only enhances mobility but also significantly reduces the risk of falls and associated injuries, improving overall quality of life.
SPINAL STENOSIS
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal, placing pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, usually caused by age-related degeneration (arthritis, bulging discs) in adults over 50. It commonly causes pain, numbness, or weakness in the lower back, neck, legs, or arms, which often worsen with standing or walking. The common treat
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal, placing pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, usually caused by age-related degeneration (arthritis, bulging discs) in adults over 50. It commonly causes pain, numbness, or weakness in the lower back, neck, legs, or arms, which often worsen with standing or walking. The common treatment options have always been physical therapy, pain medication, epidural injections, or surgical procedures.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Aging: The primary cause is degeneration, including arthritis, bony spurs, and thickened ligaments.
- Disc Herniation: Herniated or bulging discs can reduce the space for nerves.
- Congenital Conditions: Being born with a narrow spinal canal.
- Other Factors: Previous spinal injuries, tumors, or conditions like Paget's disease.
Symptoms
- Lumbar (Lower Back): Sciatica-like pain, numbness, or cramping in the buttocks and legs that improves when bending forward or sitting.
- Cervical (Neck): Pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms, hands, and legs.
- General: Difficulty walking, balance issues, and, in severe cases, bowel/bladder dysfunction.
Complications
If left untreated, severe spinal stenosis can lead to permanent numbness, weakness, chronic pain, and loss of bowel or bladder control.

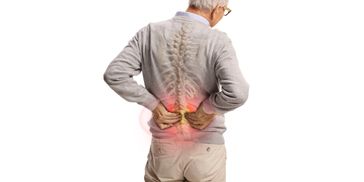
CHRONIC LOW BACK PAIN
CHRONIC LOW BACK PAIN
Chronic low back pain is defined as pain persisting for more than 3 months, often caused by muscle strain, and without proper care, leading to degenerative disc disease, arthritis, or spinal stenosis.
Causes of Chronic Low Back Pain
Chronic low back pain, which affects 619 million people globally, can stem from various structural, infla
Chronic low back pain is defined as pain persisting for more than 3 months, often caused by muscle strain, and without proper care, leading to degenerative disc disease, arthritis, or spinal stenosis.
Causes of Chronic Low Back Pain
Chronic low back pain, which affects 619 million people globally, can stem from various structural, inflammatory, and degenerative issues:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: The weakening of discs between vertebrae over time.
- Spinal Stenosis & Structural Issues: Narrowing of the spinal column or vertebrae slipping out of place (spondylolisthesis), often causing nerve compression.
- Arthritis: Specifically osteoarthritis or inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis.
- Muscular/Ligament Issues: Chronic strain or repetitive, improper movement.
- Other Conditions: Fibromyalgia, sacroiliac joint dysfunction, infections, spinal tumors, or even non-spinal issues like kidney stones.
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.